Knight Frank: House prices have probably peaked
Tom Bill, head of UK residential research at Knight Frank, predicts that house prices will fall over the next two years, following the drop in prices in September.
“It’s a fairly safe bet that UK house prices have now peaked. The impact of rising mortgage rates will begin to hit demand and spending power in coming months, which we believe will lead to a fall of 10% over the next two years for UK prices.
We may see mortgage rates fall to some extent if financial markets become more reassured by the government’s economic plan but the events of the last fortnight have been a reminder that the era of ultra-low rates is coming to an end.
Key events
Filters BETA
Mortgage rates keep rising over 6%
Average fixed mortgage rates are continuing to climb to the highest levels in over a decade, the latest data from Moneyfacts shows.
The average new two-year fixed rate – which was 4.74% on the day of the mini-budget – has climbed to 6.16%, having started the week at 5.75%.
It is a similar story with five-year fixes, with the average rate now standing at 6.07%, from 6.02% yesterday.
FT: London’s most expensive home ‘owned by Evergrande founder’
The Financial Times have a great tale this morning, that London’s most expensive house is actually owned by the head of Evergrande, the indebted Chinese property group.
The 45-room mansion overlooking Hyde Park was sold by the estate of the former Saudi Arabian crown prince Sultan bin Abdulaziz for a record-breaking £210mn in January 2020, just before the pandemic.
The FT says:
The public face of the acquisition of 2-8a Rutland Gate was Cheung Chung-kiu, a Chinese property developer whose company CC Land owns London’s “Cheesegrater” skyscraper.
However, according to five people familiar with the matter, Hui Ka Yan, the founder and chair of Evergrande and once China’s richest man, was ultimately behind it.
Given Evergrande’s plight, several people familiar with the situation have said the London property was also in effect for sale, although there was no formal process.
And here’s what £200m gets you in London:…
Never ever understood why anyone would pay £200m+ for a place that doesn’t so much “overlook Hyde Park” as sits perched atop a 4-lane carriageway (Kensington Rd, aka the A315). You even have a bus stop outside. Grim. pic.twitter.com/mfCQNx2QE6
— Stanley Pignal (@spignal) October 7, 2022

World food price have continued to drop back from their record highs hit after the Ukraine war began.
The United Nations food agency’s world price index fell for a sixth month in a row in September, down around 1%.
The drop was driven by a 6.6% month-on-month fall in vegetable oil prices, with sugar, dairy and meat prices all dipping.
Cereal prices rose, though, partly due to heightened uncertainty about whether the Black Sea Grain Initiative, under which Ukraine is exporting wheat, will continue beyond November.
???? @FAO Food Price Index drops for the 6th consecutive month in Sept, ????1.1% from Aug, but still 5.5% higher than a year ago.
45 countries flagged as in need of external assistance for food.
Global cereal production forecast for 2022 lowered by 1.7%.https://t.co/Hj6oalv7pd
— FAO Newsroom (@FAOnews) October 7, 2022
The drop in food commodities will help the developing world.
But worryingly, there are 45 countries around the world which are in need of external assistance for food, including 33 in Africa, nine in Asia, two in Latin America and the Caribbean and one in Europe.
Over in France, strikes by refinery workers are hitting supplies of fuel to some petrol stations.
Reuters has the latest:
Around 10% of petrol stations in the Paris region are having problems regarding getting enough supplies of fuel, said French government spokesman Olivier Veran today, although he reiterated that France had enough supplies of petrol overall.
Veran told BFM TV and RMC Radio.
“There are temporary problems regarding distribution.”
He said that 90% of petrol stations in the Paris had no problems in this area, although 15% of petrol stations in France overall were experiencing these “temporary difficulties.”
The French government said earlier this week that France had tapped its strategic fuel reserves to resupply petrol stations that have run dry, amid strikes by workers at refineries and depots that have stunted production and blocked deliveries.
#France, strikes at several large refineries remained ongoing and the effect of the sudden drop in supply was beginning to be felt at the pumps. Around 14% of petrol stations had run out of either #diesel or #gasoline, with some regions affected more than others. #OOTT
— Nitin Kashimpuria (@nkashimpuria9) October 7, 2022
Meanwhile in Germany, import prices rose at the fastest pace in nearly 50 years, intensifying its inflation squeeze.
Import prices in August surged by 32.7% year-on-year, the highest reading recorded since March 1974, with gas prices quadrupling.
Britain’s housing sector could soon shift from being a seller’s market to a buyer’s market, predicts Karen Noye, mortgage expert at Quilter:
Rising interest rates will simply make mortgages less affordable. This will precipitate more people to put their houses on the market so they can downsize and achieve lower monthly payments. When more houses hit the market there is naturally more choice and crucially more room for bargaining. The seller’s market, we’ve been witnessing for the past few years quickly becomes a buyer’s market.
The problem is buyers are also struggling massively with the cost-of-living crisis so demand is also set to soften, therefore those that can still afford to move will have more choice and more leverage to put in lower offers and house prices drop.
It remains to be seen how far house prices might drop but some of the housebuilders are pricing in a 20% drop, which could be an overreaction, but it is certainly not out of the question. House prices have become bloated in recent years having benefited from government policies such as the stamp duty holiday during the pandemic at a time when borrowing was very cheap.
Now the cost of borrowing is on the rise, the stamp duty cut recently brought in by Truss may serve to steady a sinking ship but it’s still likely to take on a huge amount of water.
UK economy predicted to be weak till 2024 despite Truss growth agenda

Richard Partington
Britain’s economy is expected to take until 2024 to recover to pre-Covid levels amid a slowdown for hiring and business investment, as households and businesses struggle with soaring costs.
Business leaders have said that there has been a significant decline of key economic indicators in recent weeks, with confidence among company bosses over the growth outlook collapsing to the lowest level since the depths of the Covid crisis.
Knight Frank: House prices have probably peaked
Tom Bill, head of UK residential research at Knight Frank, predicts that house prices will fall over the next two years, following the drop in prices in September.
“It’s a fairly safe bet that UK house prices have now peaked. The impact of rising mortgage rates will begin to hit demand and spending power in coming months, which we believe will lead to a fall of 10% over the next two years for UK prices.
We may see mortgage rates fall to some extent if financial markets become more reassured by the government’s economic plan but the events of the last fortnight have been a reminder that the era of ultra-low rates is coming to an end.
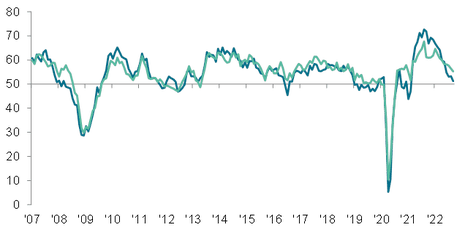
UK recruitment slowed in September as economic problems mount
The latest survey of the UK labour market also shows that the economy may be on the turn.
Growth in demand for permanent and temporary staff weakened in September, to the lowerst since February 2021, according to KPMG and the Recruitment & Employers Confederation.
The weaker economic outlook led some firms to be more cautious about hiring, and also discouraged some people from changing jobs.
A generally low unemployment rate, skills shortages and Brexit also weighed on candidate availability, the survey adds.
Claire Warnes, head of education, skills and productivity at KPMG UK, says some firms are bracing for a downturn.
Some employers, even those who anticipate that the recession may be short, are taking steps now to contain costs, including hiring freezes.
Those employers who continue to invest in their workforce, particularly upskilling, may find they weather the recession better and will be in a stronger position to benefit from the upturn as and when it comes.”
London saw the biggest rise in permanent staff appointment, while the South of England saw the first reduction in 19 months.
September’s house price fall is probably a sign of things to come, says EY ITEM Club
House prices are likely to fall by at least 5% over the next year, the EY ITEM Club says.
Martin Beck, chief economic advisor to the EY ITEM Club, says rising interest rates will push down demand, and restrict what lenders will offer.
“Weakness in prices in September is likely to be a sign of things to come, reflecting cost of living pressures and the recent rise in market interest rate expectations and mortgage rates. Granted, current market expectations for Bank Rate to rise to 5.5% by mid-2023 look too high.
“Raising rates to that level would likely prompt a substantial decline in the housing market, a deep recession and inflation eventually falling well below the Bank of England’s 2% target and potentially into negative territory. Instead, the EY ITEM Club expects Bank Rate to peak at 4%.
However, rates at that level would still significantly reduce demand for properties and decrease the size of loans that lenders can offer. Combined with the weakening economic outlook and squeezed household incomes, the EY ITEM Club expects property values to fall by 5% or more over the next year or so.
You’d think that falling house prices would help people to get onto the housing ladder.
But if mortgage rates do keep climbing, prospective first time buyers may find they’re stilll priced out of the market.
The Bank of England has already raised interest rates six times in a row, from 0.25% at the start of the year to 2.25% in September, with a very sizeable increase experted in November.
Avinav Nigam, cofounder of real estate investment platform, IMMO, says these rising borrowing costs have already had an effect on the market, and are hitting affordability.
The slowdown in house price growth for September was expected as higher interest rates in May and June kicked in, which feed through to transactions data now due to the time lag of conveyancing.
We are seeing property listings falling by 15 to 20 per cent in some parts of the UK, as uncertainty encourages property owners to delay transaction decisions.
‘The rapid pace of growth we have seen in recent years is coming to an end, partly due to recent interest rate hikes by the Bank of England and the crash of the pound following the government’s mini budget.
‘It’s predicted that house prices could correct by as much as 7 to 10 per cent in coming months. However, we don’t expect a house price growth reversal to improve the affordability of housing much due to fast rising interest rates. Mortgage lenders are starting to require consumers prove they can afford 7% interest rates, as an indication of where rates could go.
Interest rate rises are putting off new buyers
Fears of rising interest rates are cooling the markets, reports North London estate agent Jeremy Leaf:
‘New buyers are pausing for breath while they consider the likely pace and size of future interest rate hikes, so activity is reducing. The question is whether worries about rising mortgage payments outweigh the benefits of the recent stamp duty reduction, particularly for first-time buyers.
‘The mini Budget sparked a chain reaction of unintended consequences raising buyer concerns that any savings in stamp duty and other taxes would be more than offset by mortgage rates rising much more quickly and higher than expected.’
Property buying agent Emma Fildes of Brickweaver points out that annual house price inflation is now back in single figures (for the first time since January). Could the long run of growth be approaching a dead end?
According to @HalifaxBank AVG house prices decreased by -0.1% to £293,835 in September. With annual growth falling, from its long run in double digits, to 9.9% from +11.4% in Aug, could the UK property market road for growth be approaching a dead end? pic.twitter.com/23pQBLZXxa
— Emma Fildes (@emmafildes) October 7, 2022
Rising mortgage rates are the main blocker for buyers seeking to get on the property ladder and those hoping to move up it, agrees Myron Jobson, senior Personal Finance Analyst at interactive investor:
“Mortgage affordability is a mushrooming pain point for buyers. Mortgage rates have been on the up in line with increases to the Bank of England’s base rate, but rates have typically spiked by between one and two percentage points two weeks on from the mini-Budget.
The difference amounts to hundreds in pounds and pence terms, and it means that buyers can’t afford as much house as they could 14 days ago.
Wales sees fastest house price rises, but London lags
Wales remains at to the top of the table for annual house price inflation with a rate of +14.8%, down from +15.8% in the previous month, Halifax says.
The average property in Wales now costs £224,490.
London still has the slowest rate of annual growth amongst the UK nations and regions, with house prices rising by +8.1% over the last year. But properties in the capital are still the most expensive, with the average costing £553,849.
Introduction: UK house prices dropped in September
Good morning, and welcome to our rolling coverage of business, the world economy and the financial markets.
The UK housing market is slowing, and the crisis caused by the government’s mini-budget will make it worse.
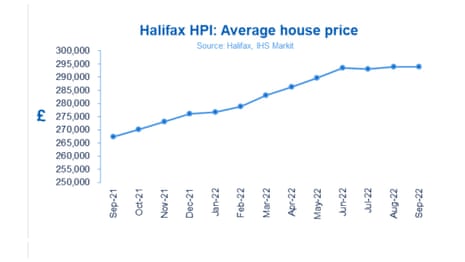
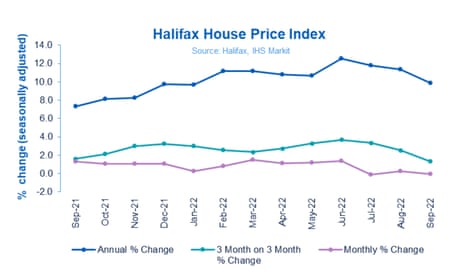
That’s the verdict from Halifax this morning. It reports that the average house prices dipped in September, by 0.1%, leaving the average property now costing £293,835.
The annual house price inflation rate slowed for the third month in a row, to 9.9% from 11.4%, the lowest rate since January.
Kim Kinnaird, director at Halifax Mortgages, reports that house prices have been largely flat since June, as the markets entered “a more sustained period of slower growth”.
Kinnaird warns that house prices will come under heavier downward pressure in the months ahead, from rising borrowing costs and the cost of living crisis:
While stamp duty cuts, the short supply of homes for sale and a strong labour market all support house prices, the prospect of interest rates continuing to rise sharply amid the cost of living squeeze, plus the impact in recent weeks of higher mortgage borrowing costs on affordability, are likely to exert more significant downward pressure on house prices in the months ahead.
Kinnaird adds that “this will undoubtedly be a cause of some concern for homeowners”, but points out that recent property price inflation has been unprecented.
It’s important to look at slower growth in this context – since the start of the pandemic average property values have risen by around +23% (almost £55,000) with detached house prices up by more than £100,000 over the same period.”
Interest rate expectations soared during the market panic following the mini-budget, with the Bank of England expected to raise rates towards 6% by next summer.
The average rate on two and five-year fixed mortgages rose over 6% this week, and is expected to keep rising. That is pricing some people out of the market, and leaving others facing a jump in repayments when they remortage.
Yesterday, UK bank bosses raised concerns over the state of the UK’s mortgage market at a high-level meeting at No 11 Downing Street.
Kwasi Kwarteng is now considering extending the government’s mortgage guarantee scheme to help the market. That scheme lets banks and building societies buy a guarantee from the government on the slice of the mortgage between 80% and 95% of the property’s value, to protect them if a property is repossessed.
Also coming up today
The main event for the markets today should be September’s Non-Farm Payroll report, which will show how many jobs were created in America last month.
Economists predict that hiring slowed, to around 250,000 from 315,000 in August, as rising US interest rates slow economic growth. A weak jobs report could encourage the US Federal Reserve to slow its interest rate rises, which might weaken the dollar.
The agenda
-
7am BST: Halifax house price index
-
7.45am BST: French trade balance for August
-
9.30am BST: UK labour productivity for Q2
-
1.30pm BST: US Non-Farm payroll report
Stay connected with us on social media platform for instant update click here to join our Twitter, & Facebook
We are now on Telegram. Click here to join our channel (@TechiUpdate) and stay updated with the latest Technology headlines.
For all the latest Business News Click Here
