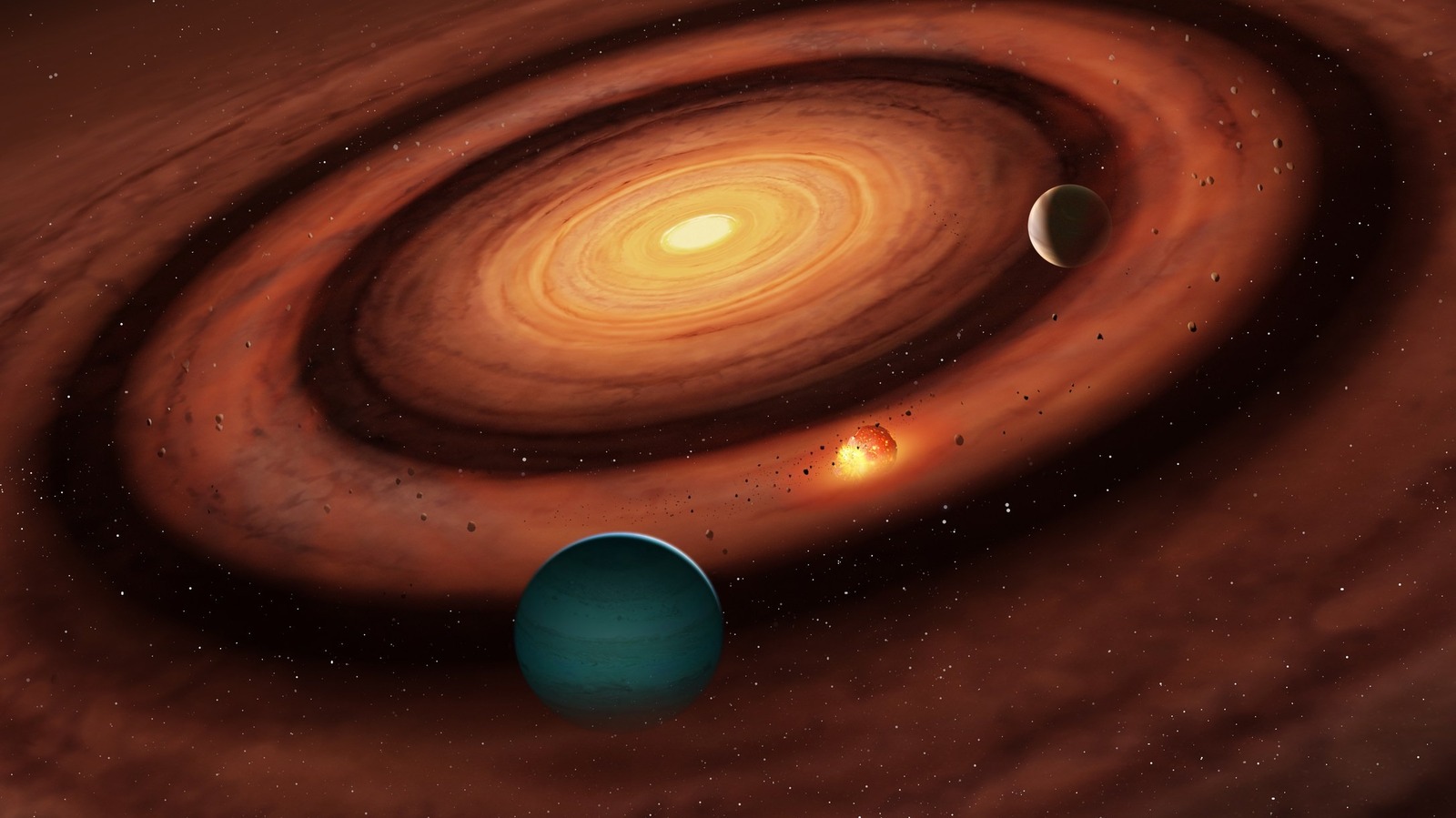
The protoplanetary theory says larger gas giants — like Saturn and Jupiter — are formed first due to the availability of gaseous raw material. And they are usually further away from their host star, while smaller and rocky planets like Venus are formed closer to the Sun.
The new theory put forth by University of Warwick scientists says that there are rings and gaps in protoplanetary discs, and it’s in these rings where sandwiched planet formation occurs. Between two giant planets in a disc, the flow of dust is restricted. But if that dust somehow manages to escape, it leads to the creation of a smaller, middle planet between the two larger siblings.
“The gaps are where we expect planets to be, and we know from theory work that planets cause dust rings to form just exterior to them,” explains Farzana Meru, an associate professor at the University of Warwick’s physics department. Notably, the researchers say they have actually found evidence of planetary architecture that supports the sandwiched formation theory.
The team says there are examples out there where a smaller planet sitting between two larger planets in a solar system, and their proportions also check out. More importantly, researchers claim that the sandwich theory could very well explain the formation of Mars and Uranus, both of which are flanked by larger planets on each side. While further research is needed, it’s an exciting new breakthrough that could unravel a new cosmic process right in the Earth’s own solar backyard.
Stay connected with us on social media platform for instant update click here to join our Twitter, & Facebook
We are now on Telegram. Click here to join our channel (@TechiUpdate) and stay updated with the latest Technology headlines.
For all the latest Gaming News Click Here
